High Availability in the Cloud: What It Is and Why It Matters
In today’s digital landscape, where businesses operate around the clock and customers expect immediate access, downtime can be catastrophic. It’s not just about inconvenience; it’s about lost revenue, damaged reputation, and a potential exodus of customers to competitors who offer a more reliable service. This is where High Availability (HA) comes into play, and its importance is magnified exponentially when we talk about the cloud.
High Availability, in its simplest form, refers to the ability of a system to remain operational and accessible even when components fail. It’s about building redundancy and resilience into your infrastructure so that if one server goes down, another seamlessly takes over. Think of it as having a backup generator for your business – when the power grid fails, the generator kicks in to keep the lights on and operations running smoothly. In the cloud, this means designing your applications and infrastructure to withstand failures and maintain performance.
This article delves into the world of High Availability in the cloud, exploring what it is, why it’s crucial for modern businesses, and how you can implement it effectively. We’ll cover the core concepts, different approaches to achieving HA, and the benefits it offers, ultimately providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how to ensure your cloud-based applications are always available when your customers need them most. Forget about apologies for downtime; let’s build a system that’s always ready.
What is High Availability?
High Availability (HA) is a system design approach that aims to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation. It’s not about preventing failures altogether (because failures are inevitable), but rather about mitigating their impact and recovering quickly. A highly available system is designed to detect failures automatically and switch over to a redundant component without significant interruption to the user. The key metric for HA is often expressed as a percentage of uptime, such as 99.99% (four nines) or 99.999% (five nines), which translates to minimal downtime per year.
Key Concepts in High Availability
Understanding these core concepts is essential for designing and implementing highly available systems:
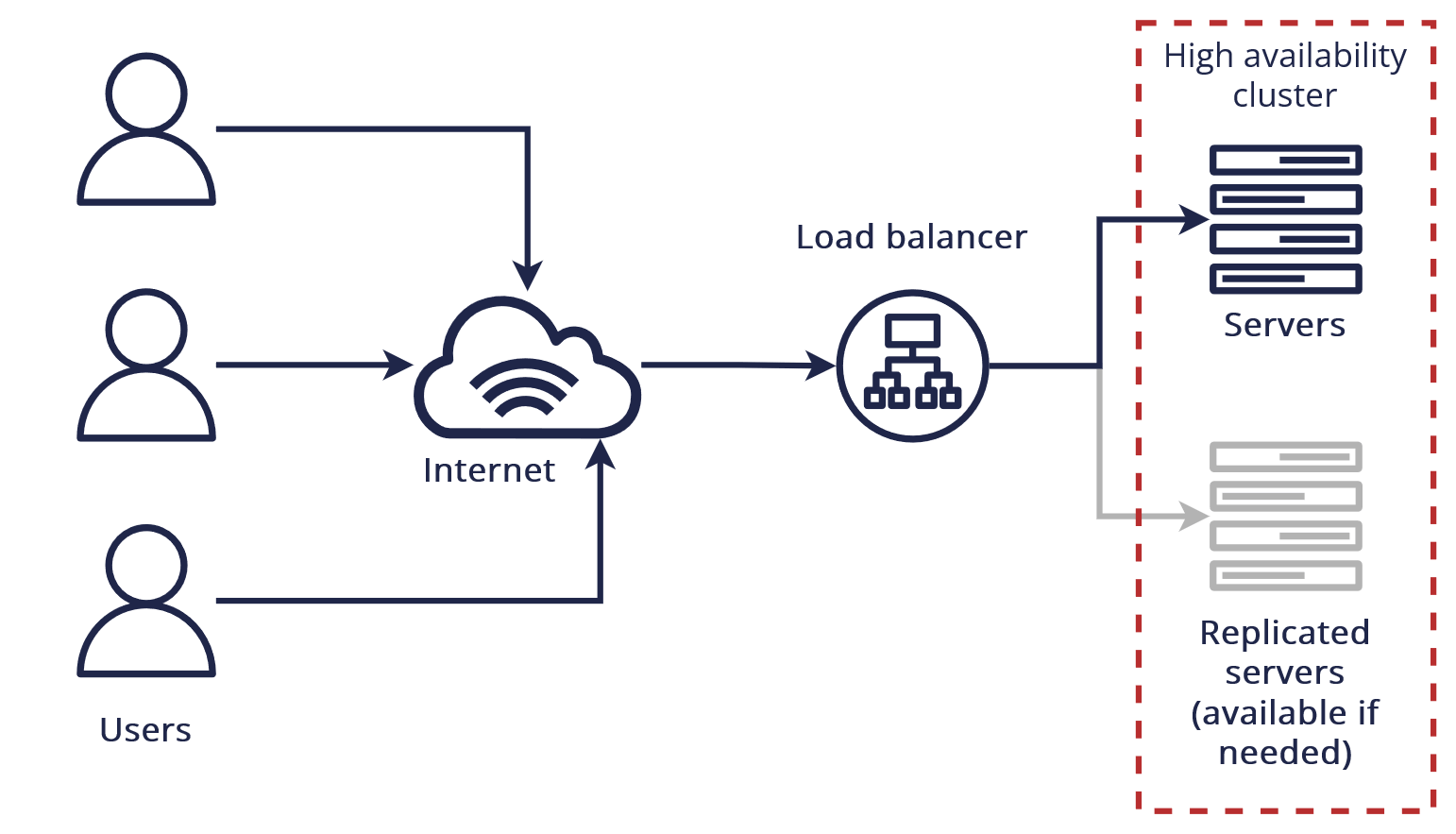
- Redundancy: This involves having multiple instances of critical components, such as servers, databases, and network devices. If one component fails, another can immediately take over its function.
- Failover: This is the automatic switching to a redundant component when a failure is detected. The failover process should be seamless and transparent to the user.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of system health and performance is crucial for detecting failures early and triggering failover mechanisms.
- Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overloaded and potentially failing.
- Replication: Creating copies of data across multiple storage devices or locations to ensure data availability even if one storage device fails.
- Fault Tolerance: Designing systems to continue operating correctly even in the presence of faults or errors. This often involves using specialized hardware and software that can detect and correct errors automatically.
Why Does High Availability Matter in the Cloud?
While HA is important for any system, its significance is amplified in the cloud for several reasons:
Increased Reliance on Cloud Services
Businesses are increasingly relying on cloud services for critical operations, from hosting websites and applications to storing data and running business processes. Any downtime in these services can have a direct and significant impact on revenue, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Global Accessibility
Cloud-based applications are often accessible to users around the world, 24/7. This means that downtime can affect a large number of users across different time zones, potentially causing significant disruption to business operations and customer experience.
Competitive Advantage
In today’s competitive market, customers have numerous choices. If your application is unreliable and prone to downtime, customers are likely to switch to a competitor who offers a more stable and dependable service. High Availability is a key differentiator that can help you attract and retain customers.
Cost of Downtime
The cost of downtime can be substantial, including lost revenue, reduced productivity, damage to reputation, and potential legal liabilities. A robust HA strategy can help minimize these costs and protect your bottom line. Some studies estimate the cost of downtime for a single critical application to be hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Certain industries, such as healthcare and finance, are subject to strict compliance and regulatory requirements regarding data availability and system uptime. High Availability is often a necessary component of meeting these requirements.
Approaches to Achieving High Availability in the Cloud
There are several approaches to achieving High Availability in the cloud, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best approach for your organization will depend on your specific requirements, budget, and technical expertise.
Redundancy and Replication
This is the most fundamental approach to HA. It involves creating multiple instances of critical components, such as virtual machines, databases, and storage devices. Replication ensures that data is copied across multiple locations, so that if one location fails, the data is still available from another. Cloud providers offer various services for replication, such as database replication and storage replication.
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overloaded. This helps to ensure that all servers are operating within their capacity and that the application remains responsive even during peak traffic periods. Cloud providers offer managed load balancing services that automatically distribute traffic based on various factors, such as server health and performance. Navigating the complexities of data residency and security is crucial, Future Cloud Compliance ensuring ongoing trust and reliability
Auto-Scaling
Auto-scaling automatically adjusts the number of resources allocated to your application based on demand. This helps to ensure that your application can handle unexpected spikes in traffic without experiencing performance degradation or downtime. Cloud providers offer auto-scaling services that automatically add or remove virtual machines based on predefined rules.
Geographic Distribution
Distributing your application across multiple geographic regions can protect against regional outages, such as power failures or natural disasters. This involves replicating your application and data across different data centers in different geographic locations. Cloud providers offer services for deploying applications and data across multiple regions.
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance involves designing systems to continue operating correctly even in the presence of faults or errors. This often involves using specialized hardware and software that can detect and correct errors automatically. For example, using RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) for storage can protect against disk failures.
Implementing High Availability: Best Practices
Implementing High Availability effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to follow:
Define Clear Availability Requirements
Start by defining your organization’s availability requirements. What level of uptime do you need to achieve? How much downtime can you tolerate? What are the potential costs of downtime? Answering these questions will help you determine the appropriate HA strategy for your needs.
Design for Failure
Assume that failures will occur and design your system to handle them gracefully. This means building in redundancy, implementing failover mechanisms, and continuously monitoring system health.
Automate Everything
Automate as much of the HA process as possible, including monitoring, failover, and recovery. This will reduce the risk of human error and speed up the response to failures.
Test Regularly
Regularly test your HA mechanisms to ensure that they are working correctly. This should include simulating failures and verifying that the system can recover as expected. Consider using chaos engineering principles to proactively identify and address potential weaknesses in your system.
Monitor Continuously
Continuously monitor your system’s health and performance to detect failures early and trigger failover mechanisms. Use monitoring tools to track key metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network latency. The journey toward modernization often involves embracing architectures, with Cloud Native Cloud representing a significant shift in how applications are built and deployed
Use Managed Services
Take advantage of managed services offered by cloud providers, such as managed databases and load balancers. These services often have built-in HA features that can simplify your implementation and reduce your operational burden.
Document Your Procedures
Document your HA procedures thoroughly so that anyone on your team can understand how to respond to failures. This documentation should include step-by-step instructions for failover, recovery, and troubleshooting.
Benefits of High Availability
Investing in High Availability offers numerous benefits for your organization:
Reduced Downtime
The most obvious benefit is reduced downtime, which translates to increased revenue, improved productivity, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Customers expect reliable service. High Availability ensures that your application is always available when they need it, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. Many businesses are finding that Cloud Solutions Help to streamline operations and improve efficiency
Enhanced Reputation
A reliable application enhances your organization’s reputation and builds trust with customers and partners.
Increased Revenue
By minimizing downtime, High Availability helps to protect your revenue stream and prevent lost sales.
Reduced Costs
While implementing HA may require an initial investment, it can ultimately reduce costs by preventing costly downtime and minimizing the impact of failures. Many organizations are evaluating new technologies, Cloud Solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability and cost-effectiveness
.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
HA can help you meet compliance and regulatory requirements related to data availability and system uptime.
Conclusion
High Availability in the cloud is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for modern businesses. By understanding the core concepts, implementing appropriate strategies, and following best practices, you can ensure that your cloud-based applications are always available when your customers need them most. The investment in HA is an investment in the reliability, resilience, and ultimately, the success of your business in the cloud.
Don’t wait for a major outage to realize the importance of High Availability. Start planning and implementing your HA strategy today to protect your business from the potentially devastating consequences of downtime. Remember, the best time to prepare for a crisis is before it happens.
By embracing High Availability, you’re not just building a more resilient system; you’re building a more resilient business, ready to face the challenges and opportunities of the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about High Availability in the Cloud: What It Is and Why It Matters
What is high availability (HA) in cloud computing, and how does it differ from fault tolerance?
High availability in cloud computing refers to a system’s ability to remain operational and accessible for a specified period of time. It is typically measured as a percentage of uptime, such as 99.99% (four nines) or 99.999% (five nines). HA is achieved through redundancy and failover mechanisms. If one component fails, another takes over seamlessly to minimize disruption. Fault tolerance, on the other hand, goes a step further. It aims to prevent failures from occurring in the first place by using redundant components that can continue operating even when one fails. While both aim for continuous operation, HA focuses on rapid recovery after a failure, whereas fault tolerance focuses on preventing failures altogether. A highly available system might experience brief downtime during a failover, while a fault-tolerant system should ideally experience no downtime.
Why is achieving high availability so important for businesses using cloud services, and what are the potential consequences of downtime?
Achieving high availability is crucial for businesses using cloud services because downtime can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. For example, an e-commerce site that experiences downtime can lose sales, frustrate customers, and damage its brand image. Beyond lost revenue, downtime can also disrupt internal operations, impacting employee productivity. The cost of downtime varies widely depending on the size and nature of the business, but studies show that it can cost companies thousands or even millions of dollars per hour. Moreover, prolonged downtime can erode customer trust and loyalty, potentially leading them to switch to competitors. In regulated industries, downtime can also result in compliance violations and penalties. Investing in HA solutions is therefore a critical business decision to mitigate these risks and ensure business continuity.
What are some common strategies and technologies used to implement high availability in a cloud environment, and how do they work together?
Several strategies and technologies contribute to implementing high availability in the cloud. These include: Redundancy (duplicating critical components like servers and databases), Load Balancing (distributing traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload on a single server), Failover Mechanisms (automatically switching to a backup system when the primary system fails), Monitoring and Alerting (continuously monitoring system health and alerting administrators to potential problems), and Automated Recovery (using scripts or tools to automatically restore services after a failure). Cloud providers offer various services to support these strategies, such as virtual machines, load balancers, and managed databases with built-in replication and failover capabilities. For instance, using multiple availability zones within a region ensures that if one zone experiences an outage, the application can continue running in another zone. These technologies work together to create a resilient and highly available infrastructure.






